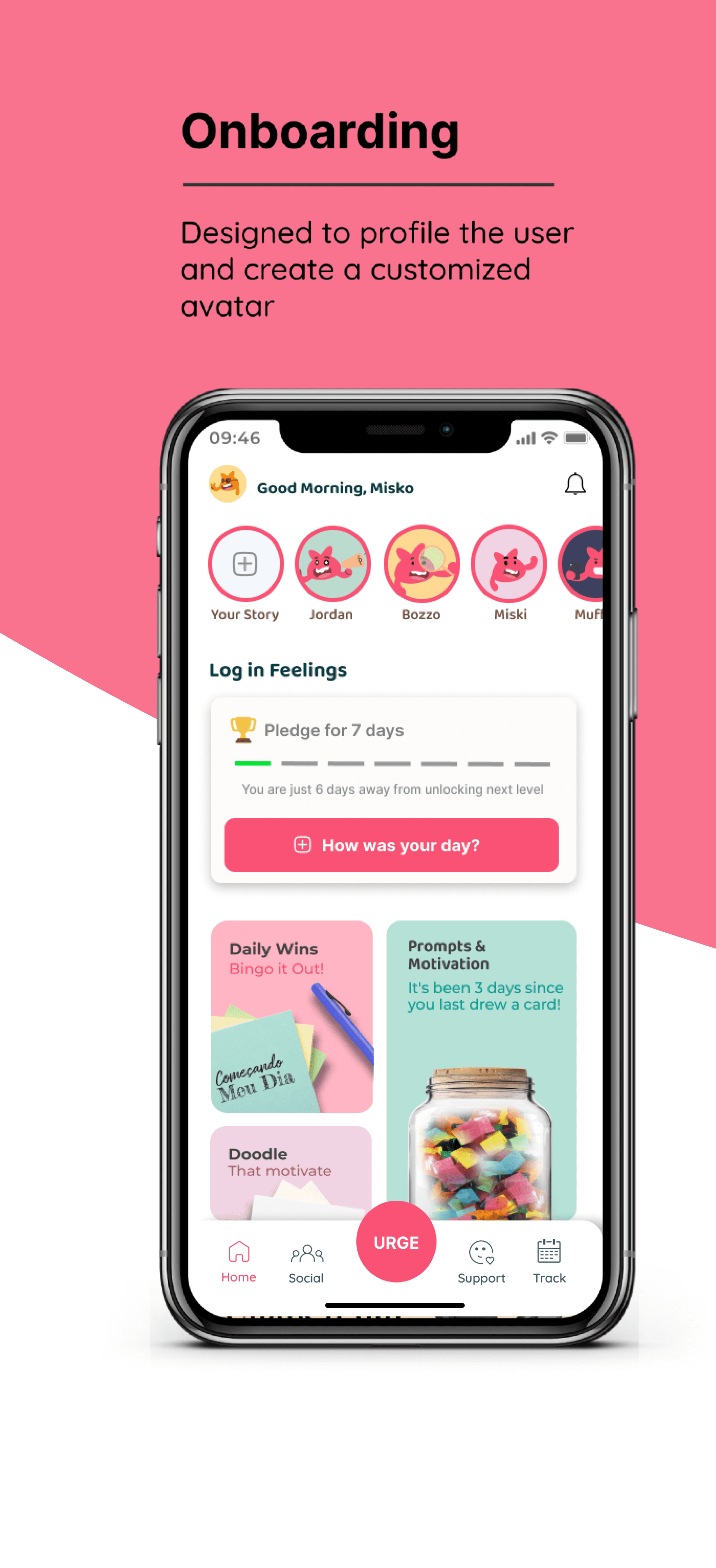
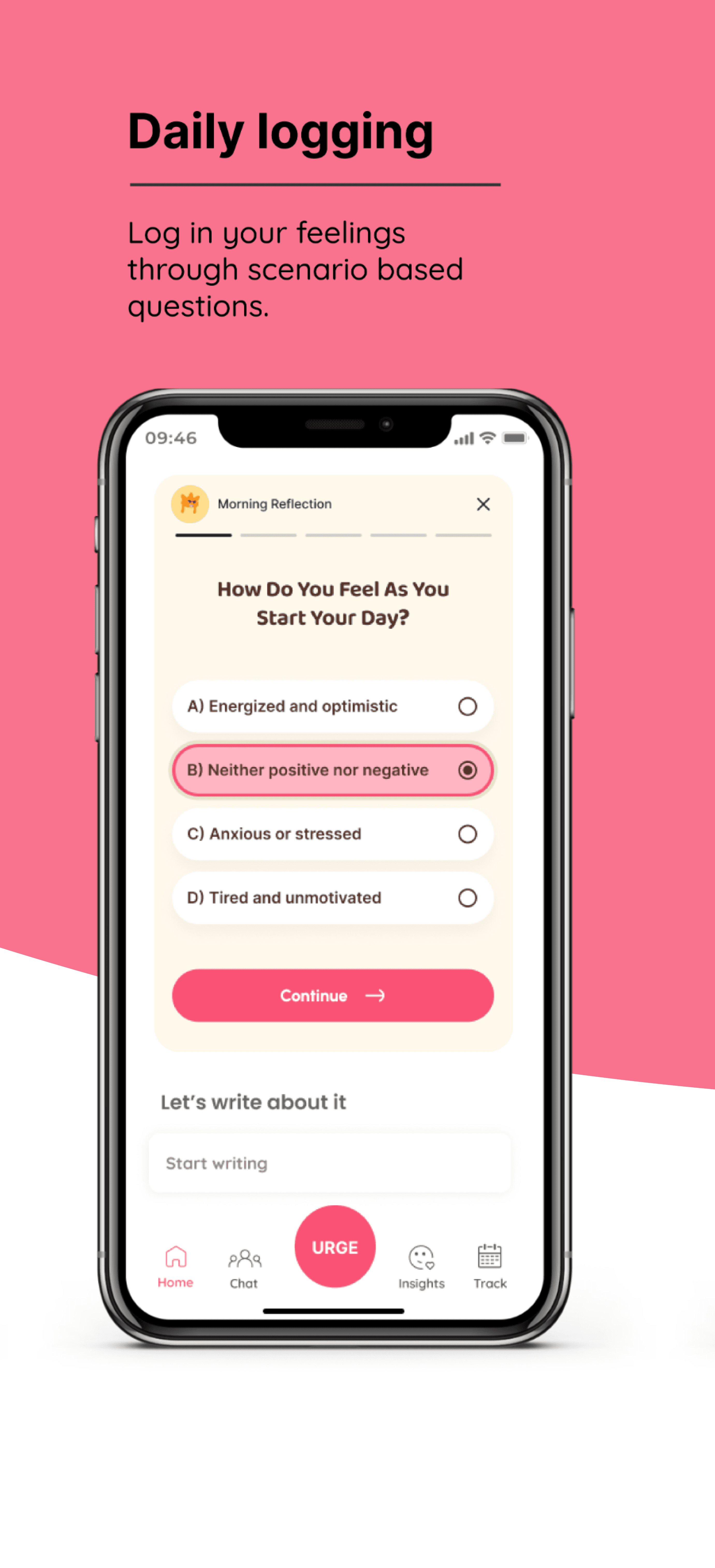
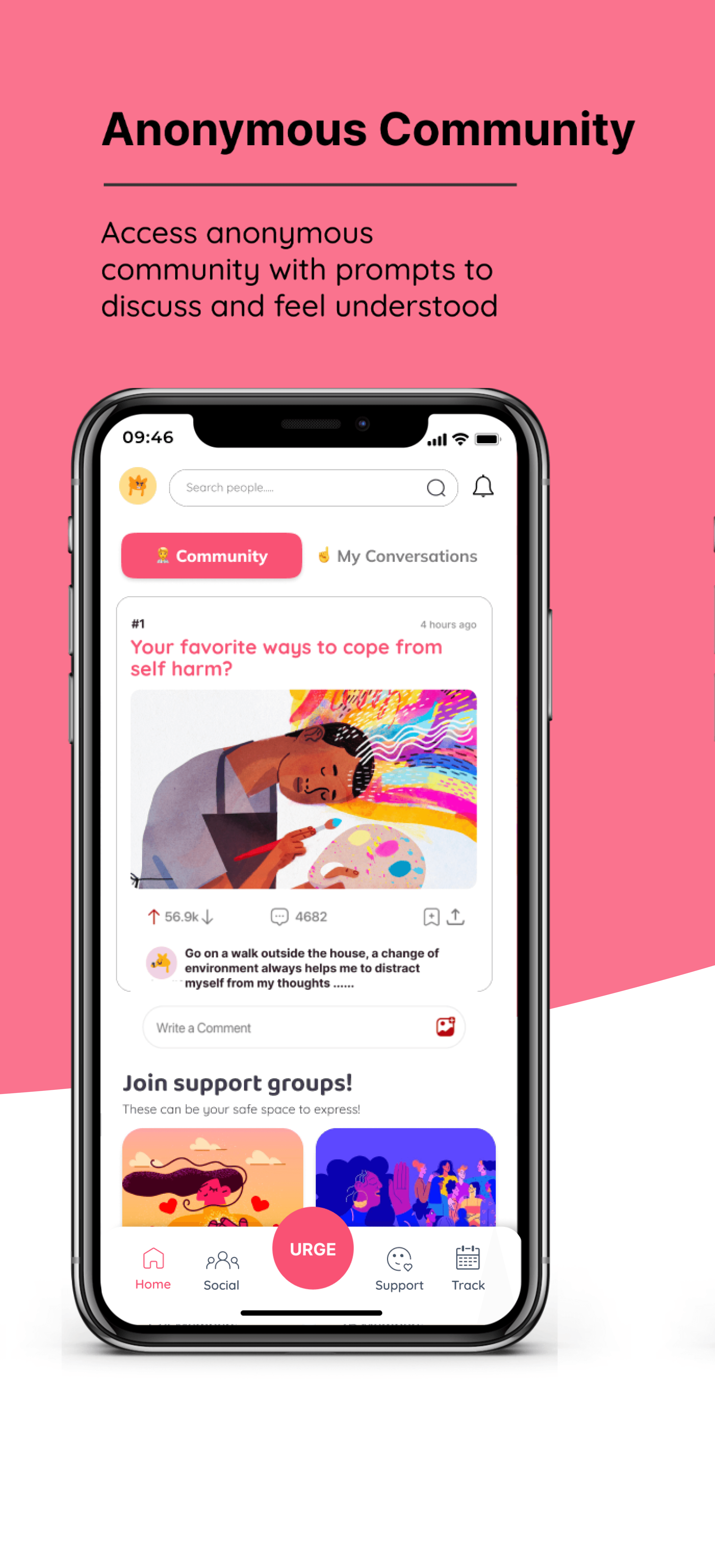
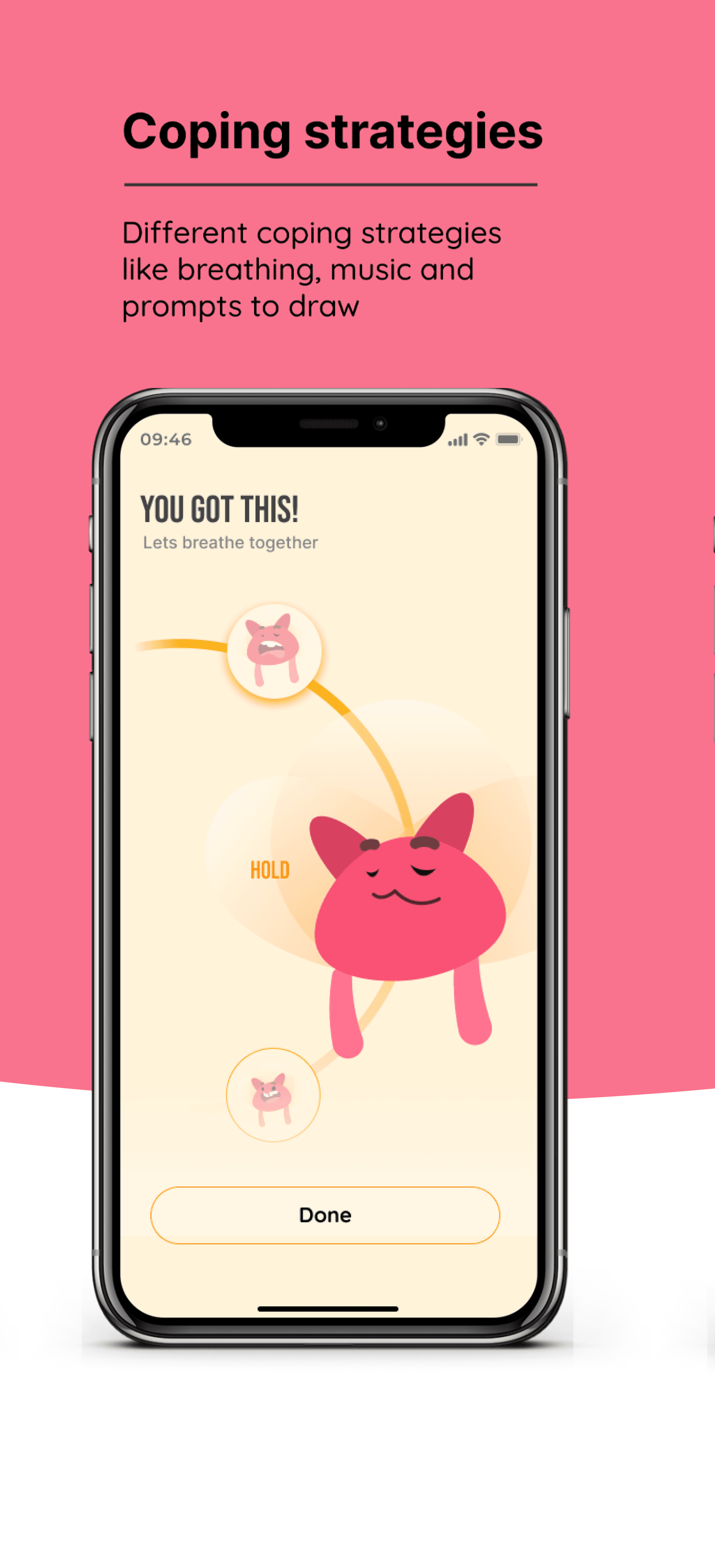
THE SELF GAUGE: DESIGNING FOR WELLBEING
Mental Health,
reimagined for Teenagers
TARGET AUDIENCE
Teenagers between 12-18yrs facing self harming tendencies
PARTICIPANTS
19 teenagers | 17 end users | 3 Adolescent counselors | 1 child graphologist | 1 psychotherapist.
Problem
Around 13.2% of college students in Indian urban cities resort to cutting or carving skin as a form of intentional self-harm ,with significant long-term implications on personal and social well-being.
Solution Approach
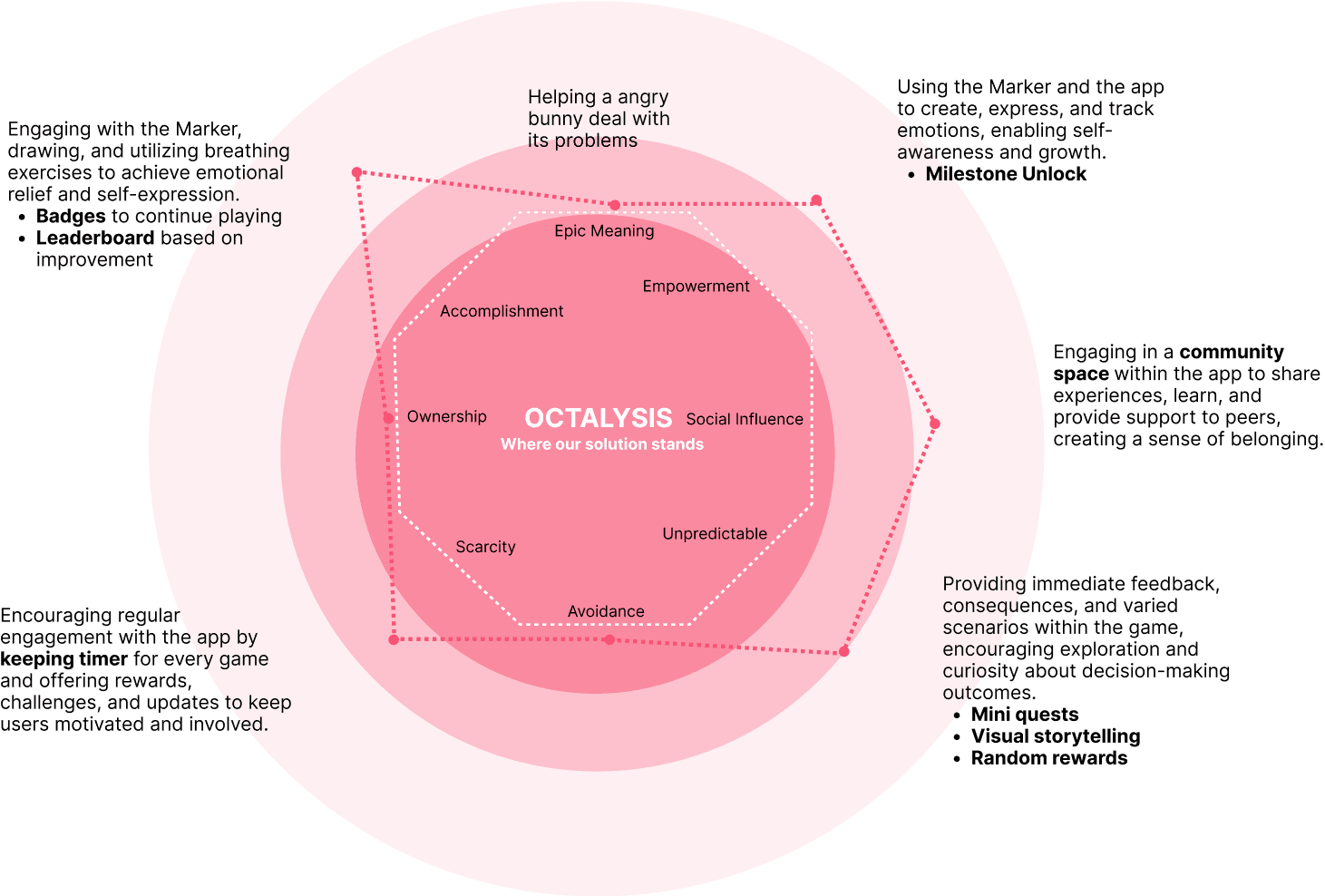
Main Goal is to enable users to gain a deeper understanding of their emotional patterns and cultivate healthier coping mechanisms, addressing a significant market gap and supporting individuals on their path to recovery.
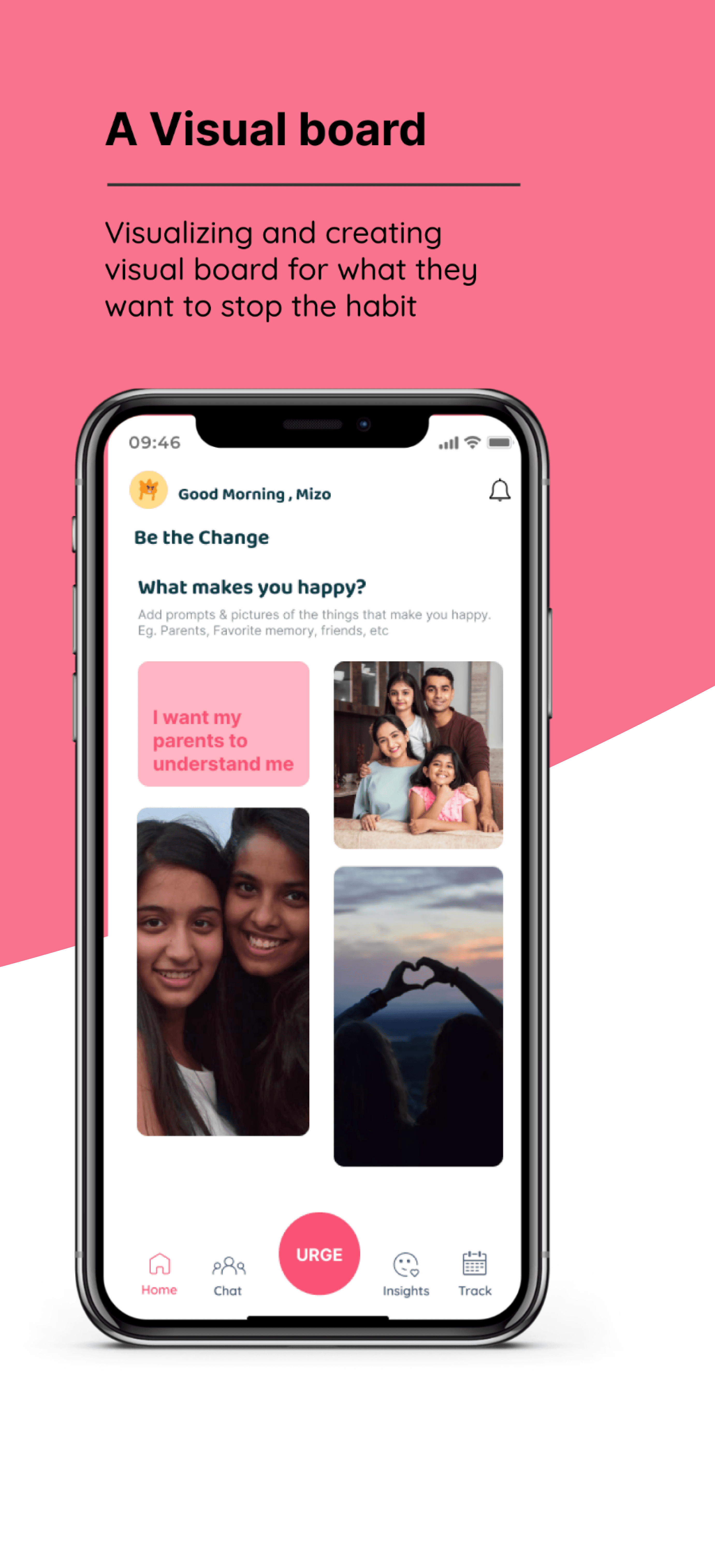
EXPLORATION
A companion for teenagers in breaking the habit of self-harm , by introducing a more effective coping mechanism.
Secondary Insights
Causes of Self harm
Emotional Outlet
Teens may resort to self-harm to express and manage overwhelming emotions, often as a response to feeling misunderstood or criticized by peers and family.
Unmet Expectations
Unmet expectations and intense frustration can lead to self-harm as a coping mechanism.
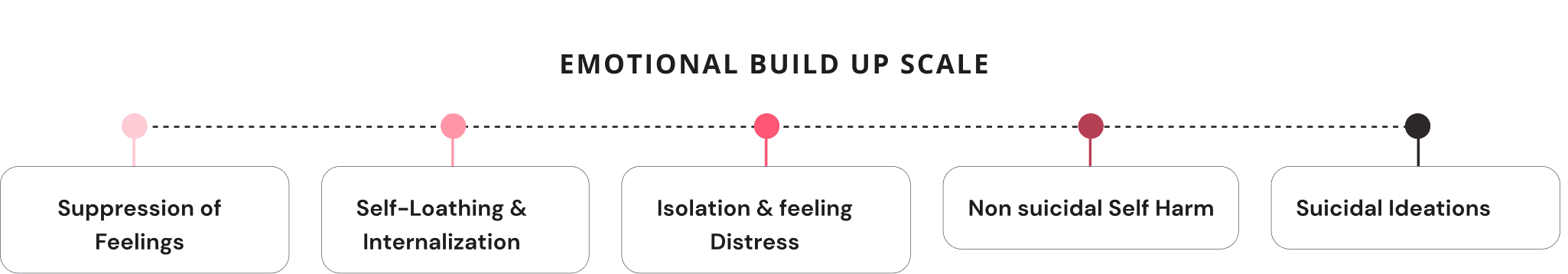
Habitual Coping Mechanism
Over time, this behavior can become habitual and compulsive, providing temporary relief from emotional distress and creating a challenging cycle to break.
desigN process
Understanding the ‘Immediate relief’ mindset
Self harm As a negative habitual coping mechanism

PAIN POINTS
The weight of expectations leads to immense emotional stress and a feeling of being trapped.
COPING STRATEGIES
Withdrawal from social interactions as a way to deal with emotional turmoil.
Can’t express and represses anger leading to self harm

PAIN POINTS
Feelings of frustration, anger, and emotional distress build up due to suppressed emotions and unresolved conflicts.
COPING STRATEGIES
Avoiding confrontations or difficult conversations to prevent further conflict.
Want distraction/Instant relief from emotional pain leading to self harm
PAIN POINTS
High expectations from parents and teachers create immense stress and a sense of inadequacy.
COPING STRATEGIES
Bottling up emotions due to the inability to express herself openly or seek support.
Primary Insights
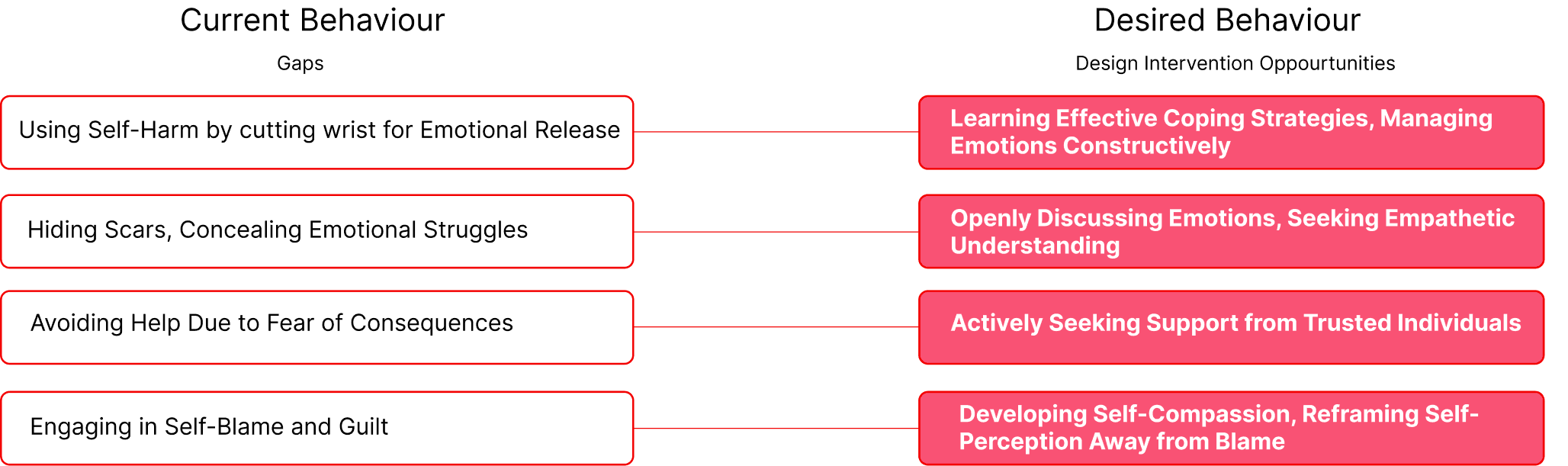
Feeling misunderstood, peer/family criticism, and unmet expectations are key anger triggers in teens.
Teen coping mechanisms for anger control may evolve into lifelong compulsive behaviors.
Teens, fearing judgment, may resort to self-harm as an alternative emotional outlet
Teens, when overwhelmed by even minor triggers, resort to self-harm as a habitual coping mechanism.
Teens can’t express and represses anger due to strict parents leading to self harm.
Teens often resort to self-harm as a distressing yet immediate method to seek relief from emotional pain.
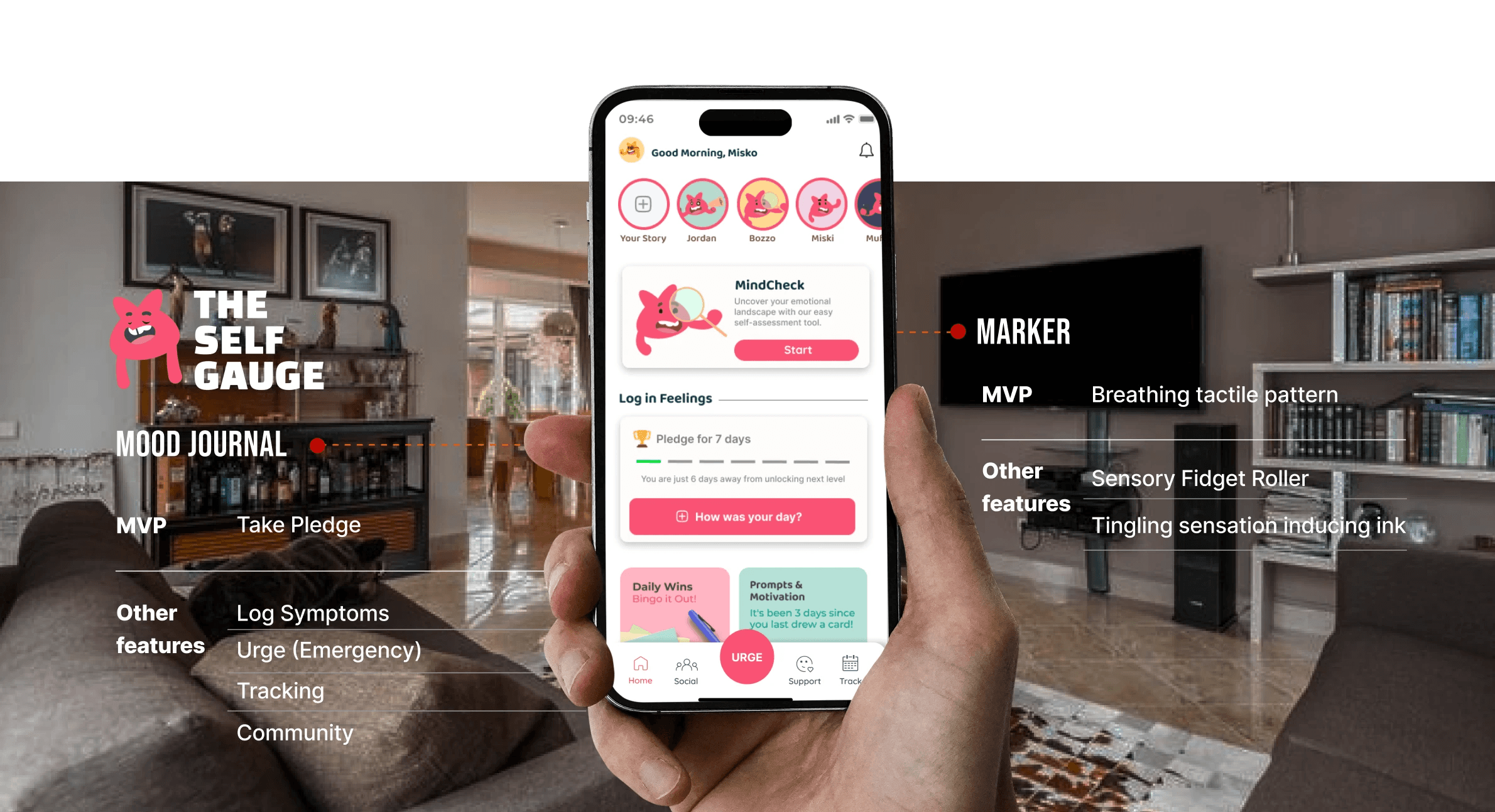
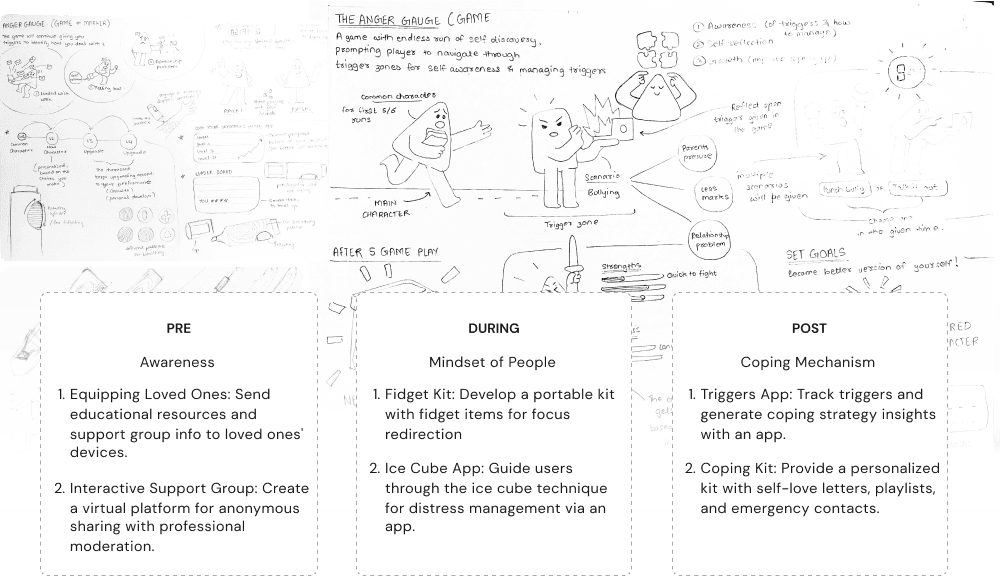
PROTOTYPING
Conceptualization
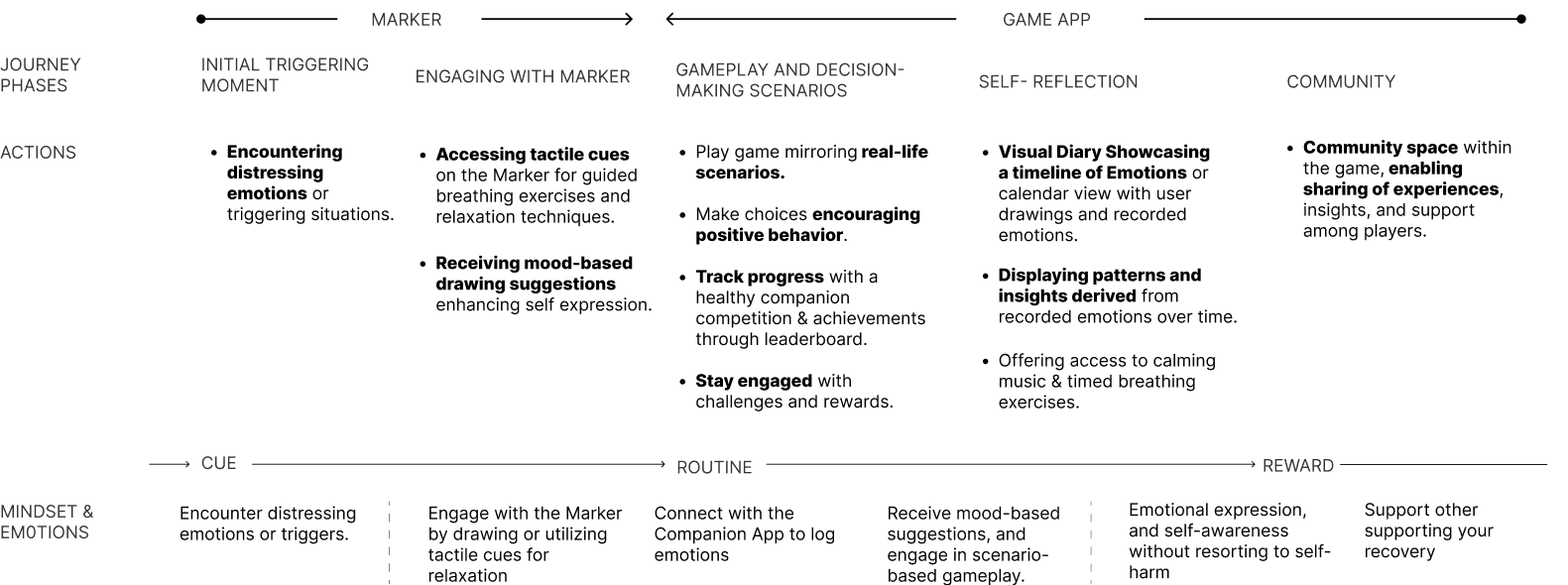
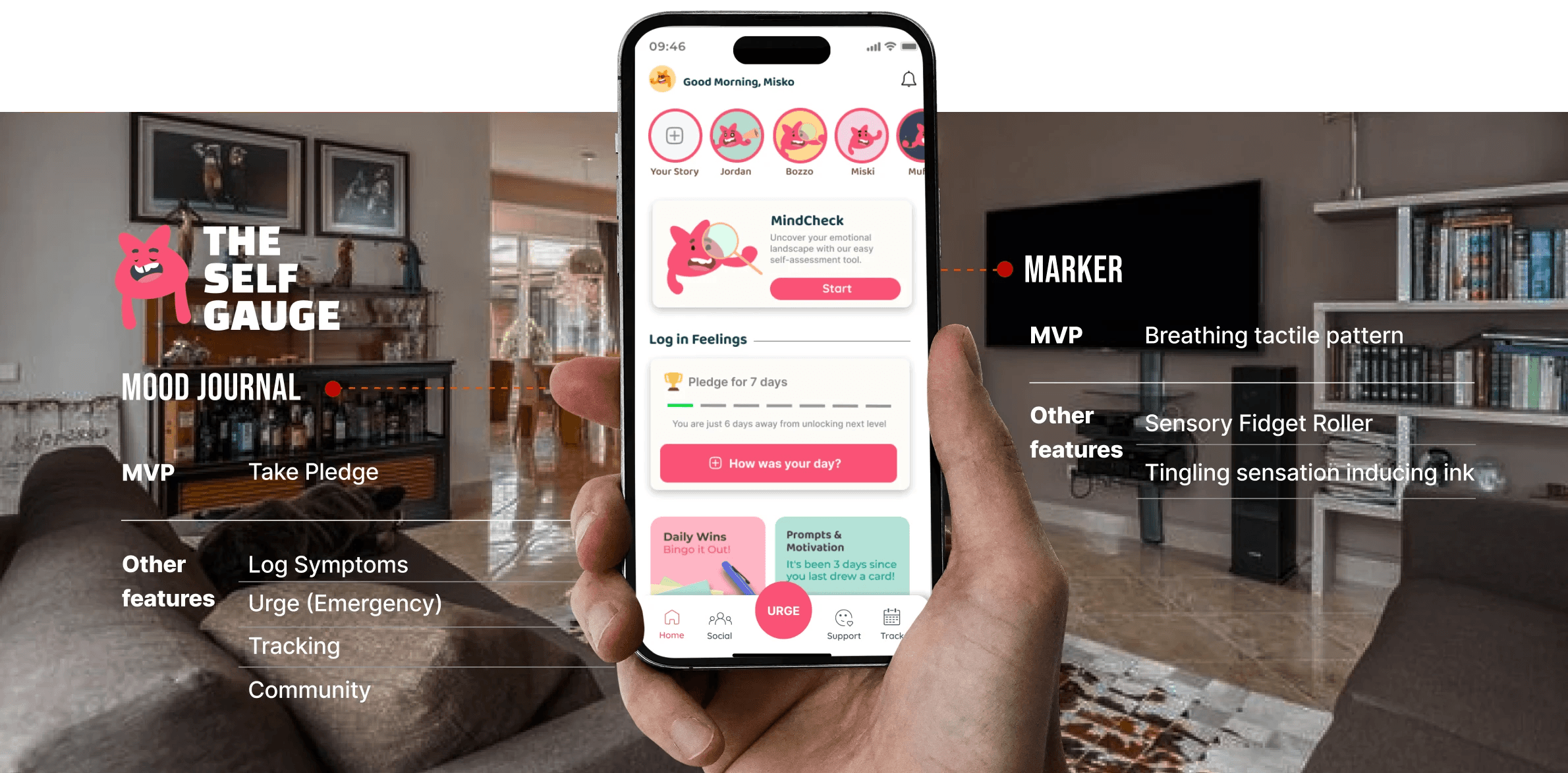
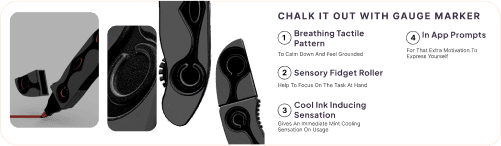
FINAL SOLUTION
Breaking The Chain
DESIGN VALIDATION
UT Assessment
UI Findings
Colour Contrast
Better accuracy to performing action was observed with colour contrast added to the screens.
Familiar Components
Accessible Keyboard added to the task flow to help the users recognise the task stage & achieve a more familiar app usage was appreciated by the users, increasing their accuracy in later stages of the task.
Excessive Screen reader Assistance
Elements with same functionality could be better placed to be read together, decreasing missed interaction opportunities (Action text Fields and its assertive labelling being read at separate swipe stages by the user caused confusion on task continue window).
Speaker Audio Limitation
Unavailability of Speaker Audio based interactions such as Audio Search & Talk back feature couldn’t accurately provide user Navigation experience designed for them. At this stage an external prototype was used.
Camera setup
The front camera being set as the primary caused interruptions and discomfort due to the screen reader announcing its activation. Switching to the rear-view camera as the default reduced these unexpected notifications.
Learning Curve
Users are optimistic that the the learning curve of the app's UI will be positively influenced by practice and familiarity based on the feedback collected by users at the completion of their task.
Screen Reader Findings
#1 Sequenced screen reader:
Screen reader sequence defined on each page based on patterns previously identified helped users to confidently recognize stages and action outcomes better with lesser assistance.
#2 Customization Options
Users expressed the desire for more customization options to tailor the app according to their preferences and specific accessibility requirements.
#3 Feature Prioritisation
Users provided valuable feedback on prioritising certain features, such as real-time updates and indoor maps, which they considered more essential for their needs.
#4 One swipe reader
Users were able to understand cards with one swipe continuous screen reader and preferred it to earlier segments.
#5 Learning Curve
Users are optimistic that the learning curve of the app's UI will be positively influenced by practice and familiarity based on the feedback collected by users at the completion of their task.
CONCLUSION
Improvement Scope
To enhance user experience and accessibility, we identified several areas for improvement:
Shorter Description
Need for shorter and direct descriptions on elements to provide a smoother experience
Tactile-less feedback
Absence of drew attention as an area where improvements were warranted to ensure a more intuitive and comprehensible user experience
Revaluate Limitations
There is still need for more refined study on acceptance of prototype platform accessibility limitations and ways to make the existing UI more accessible to the users.